- Published on
聊聊前端的路由方案
- Authors

- Name
- noodles
- 每个人的花期不同,不必在乎别人比你提前拥有
概要
本文主要梳理前端路由的实现方案,按照如下的逻辑进行梳理: 前置知识 => 路由方案现状 => 从源码的解读理解前端路由的实现过程
前置知识
history
| 方法(属性) | 含义 |
|---|---|
| history.length | 只读, 代表当前会话历史的长度 |
| history.state | 只读, 代表当前会话栈顶的state |
| history.go(number) history.forward() history.back() | 从当前会话加载特定的页面,会触发popstate事件 |
| pushState(state, title, url) | 在当前会话的添加一个新的记录(关联state) url参数需要保证同源策略 |
| replaceState(state, title, url) | 替换当前会话栈顶的记录(不会增加history长度,关联state) url参数需要保证同源策略 |
history相关事件
当用户触发浏览器动作或者js调用history.back/history.forward/history.go方法时,会触发popstate事件。
hash相关事件
- 当url片段标识符改变(#xxx), 会触发hashchange事件。
- 当设置与当前不同的hash片段的时候,会在当前会话中添加一个新的记录。
路由方案现状
| 方案 | 原理 | 优缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 基于history实现的路由方案 | 使用history相关事件和方法完成路由的切换 | history可以设置同源下的任意url,需要注意与服务端结合的场景,防止出现404 |
| 基于hash实现的路由方案 | 使用hash相关事件完成路由的切换 | hash只能改变当前url的#,有局限性 |
从源码的了解路由的实现过程
以下源码分析了history路由的实现过程,源码涉及history, react-router.整体的实现逻辑如下
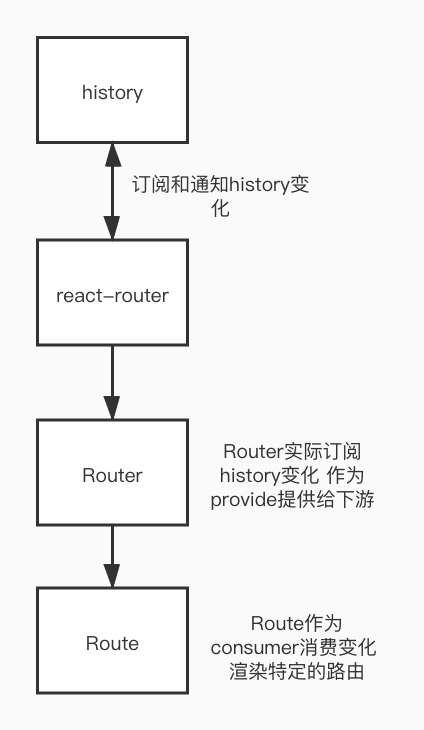
下面代码是在react项目中使用history路由实现的一个例子,它能实现根据特定的path来渲染对应的组件。
import './App.css';
import React from 'react'
import {
BrowserRouter as Router,
Switch,
Route,
} from "react-router-dom";
function App() {
return (
<Router >
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/">
<div>home</div>
</Route>
<Route path="/about">
<div>about</div>
</Route>
<Route path="/dashboard">
<div>dashboard</div>
</Route>
</Switch>
</Router>
);
}
export default App;
react-router/packages/react-router-dom/modules/BrowserRouter.js
import React from "react";
import { Router } from "react-router";
import { createBrowserHistory as createHistory } from "history";
class BrowserRouter extends React.Component {
history = createHistory(this.props);
render() {
// 初始化browser history 可以推断出路由的切换逻辑是history与Router结合的实现
return <Router history={this.history} children={this.props.children} />;
}
}
export default BrowserRouter;
packages/index.ts
// 在最后执行跳转的时候 会执行所有的listen函数
function applyTx(nextAction: Action) {
action = nextAction;
[index, location] = getIndexAndLocation();
listeners.call({ action, location });
}
let history: BrowserHistory = {
// 以下为主要的跳转函数,在实现跳转逻辑的时候都调用了applyT方法。
push,
replace,
go,
back() {
go(-1);
},
forward() {
go(1);
},
// listion方法用于增加路由切换的监听函数
listen(listener) {
return listeners.push(listener);
},
// block方法允许传入一个block函数,在路由跳转的时候会执行所有的blocker函数
block(blocker) {
let unblock = blockers.push(blocker);
if (blockers.length === 1) {
window.addEventListener(BeforeUnloadEventType, promptBeforeUnload);
}
return function() {
unblock();
if (!blockers.length) {
window.removeEventListener(BeforeUnloadEventType, promptBeforeUnload);
}
};
}
};
return history;
从上面history源码看出,history这个库主要是维护history的相关状态(state, location, hash)并且增加路由跳转的告知能力.
react-router/packages/react-router/modules/Router.js
import React from "react";
import HistoryContext from "./HistoryContext.js";
import RouterContext from "./RouterContext.js";
class Router extends React.Component {
static computeRootMatch(pathname) {
return { path: "/", url: "/", params: {}, isExact: pathname === "/" };
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
location: props.history.location
};
this._isMounted = false;
this._pendingLocation = null;
if (!props.staticContext) {
// 这里订阅了history的变化并且在变化的之后更新location
this.unlisten = props.history.listen(location => {
if (this._isMounted) {
this.setState({ location });
} else {
this._pendingLocation = location;
}
});
}
}
componentDidMount() {
this._isMounted = true;
if (this._pendingLocation) {
this.setState({ location: this._pendingLocation });
}
}
render() {
return (
// 将location作为context 在需要订阅的位置获取 Route消费location完成特定children的渲染。
<RouterContext.Provider
value={{
history: this.props.history,
location: this.state.location,
match: Router.computeRootMatch(this.state.location.pathname),
staticContext: this.props.staticContext
}}
>
<HistoryContext.Provider
children={this.props.children || null}
value={this.props.history}
/>
</RouterContext.Provider>
);
}
}
export default Router;